Poster session

Discover the latest GS1 Healthcare initiatives presented by GS1 Member Organisations, USAID and GS1 Global Office
Learn about case studies featuring recent, innovative implementations in several countries along with the latest trends in healthcare from GS1 Global Office.
Building interoperability through unique identification and data standards
One of the challenges facing health services today is how to ensure that as they digitise they achieve interoperability, support for future needs and scalability.
By starting with implementing GS1 & ISO standards-based patient and care provider identification, ACT Health have been able to gradually introduce new systems that clearly monitor, manage and record all activities across the care process. From the point a patient walks into a care facility, and throughout their healthcare journey, standards safeguard the patient by improving accuracy and increasing efficiency. GS1 identification and data standards are enabling ACT Health to build systems architecture that supports the needs of today and the future.
Pharmaceutical Supply Chain Modernisation at Hong Kong Hospital Authority
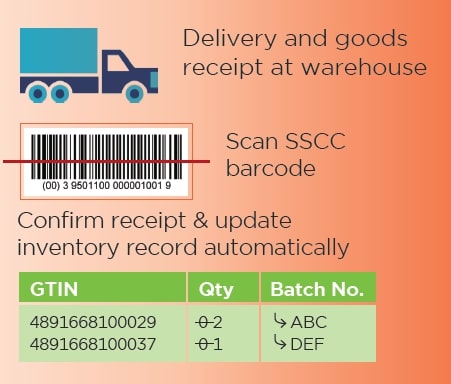
The digitalization of the ordering and receipt process for 43 public hospitals and 73 public out-patient clinics in Hong Kong was realized by ezTRADE, a standards-based platform developed by GS1 Hong Kong.
EzTrade facilitates the electronic data interchange of the order, delivery, and receipt transactions among public hospitals and suppliers. It streamlines the receiving and invoicing process by capturing the SSCC and GTIN barcode when scanned with smart devices. Currently, 81% of suppliers have adopted ezTRADE which covers about 90% of transaction orders. This digitalization process not only enhances operational efficiency, but also enables track and trace functionality and facilitates efficient product recalls, thus enhancing patient safety.
GS1 Japan Scan: New app for a simple check of GS1 Barcodes
This new app will facilitate promotion of the appropriate use of GS1 standards and prevent problems caused by barcodes not aligned with the GS1 standards.
It has been more than 10 years since the healthcare industry adopted GS1 barcodes in Japan. However, we still come across some barcodes that do not comply with GS1 standards. For instance, when no function 1 is encoded in the first position. Considering these circumstances, GS1 Japan launched a new app called “GS1 Japan Scan.” The app enables users to simply check whether their barcodes fulfil the requirements of the GS1 standards and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. GS1 Japan hopes that the new app will facilitate promotion of the appropriate use of GS1 standards and prevent problems caused by barcodes not aligned with the GS1 standards.
Singapore’s National University Hospital (NUH) - How global standards for barcodes in product identification combined with IT reduce preventable errors & enable full product traceability - keys to patient safety
This poster gives an overview of Singapore National University Hospital’s (NUH)’s program to address errors in medication use processes.
Global standards for product identification, coupled with information technology in medication use, will reduce preventable errors, thereby enabling full product traceability which is the key to patient safety. NUH modified and re-invented their processes, where possible including reliance on supplier applied (global standard) barcodes, to facilitate medication traceability through the hospital processes. Today, the hospital has full closed-loop drug distribution, closed loop in-patient automated medication management, and outpatient pharmacy automation, all barcodes for medication identification.
GS1 barcodes on medical devices improve resource management and enhances patient safety
Besides normal medical processes, Kaohsiung Armed Forces General Hospital (KAFGH) also offers emergency relief and wartime aid.
The deans of KAFGH always strive to discover medical skills and innovative technology in order to improve medical quality and medical efficiency. In addition to refining medical processes, KAFGH also aligned with Unique Device Identification (UDI) and put attention on the medical management of implants. At the time the Taiwan Food and Drug Administration (TFDA) began to promote UDI, KAFGH developed a medical device management system and successfully applied the concept in clinical sites. UDI not only helps improve efficiency, but also enables the application of big data analysis for medical activities, which has a real impact in saving human lives, resources and reducing cost.
Reducing ‘never events’ using GS1 Standands
This poster shows the use of real-time event data in an innovative way to warn medical professionals if they’re about to make a bad decision.
Using a data stamp for every person, every product and every place, this solution looks at all available information against the existing patient, procedure and product data. Using open, interoperable GS1 standards together with data the Trust already has, North Tees and Hartlepool NHS Foundation Trust are making sure that when they scan once, they get data they can use many times.
Surgical path way
This poster represents a patient pathway through a hospital.
The GS1 standards enable better quality patient care through unambiguous identification of every patient, every product and every place. This enables healthcare providers and suppliers to provide improved patient safety, enhanced clinical effectiveness and drive operational efficiencies. This poster brings to life the ability to scan once and use the data many times.
The GDSN Opportunity for Global Health
The USA I.D Global Health Supply Chain Program Procurement and Supply Management project is implementing the GS1 Global Data Synchronization Network to exchange item master data to serve as the basis of their product catalogue.
GHSC-PSM’s vision is that all of our partners in procurement, trade, and service delivery will leverage the GDSN to operate off of the same high-quality master data populated and maintained by our suppliers. The benefits are significant: improved data visibility, increased operational efficiency, and more secure supply chains, to reach our collective goal of ensuring patient safety.
GS1 Healthcare Strategy 2018-2022
Learn about GS1 Healthcare’s 2018-2002 strategy, harnessing the power of open, global standards to address the challenges of healthcare and benefit patients worldwide.
The strategy aims to: ensure that current activities are maintained to drive deeper standards implementation; to further enhance the already increased focus on hospitals and retail pharmacies and bring the patient increasingly into focus; and to allow monitoring, influencing and action, where appropriate, to engage with emerging technology developments.
GLN implementation Guide
As the healthcare industry continues to realise the value of implementing GS1 standards and finds opportunities for efficiencies in internal processes, supply chain operations, logistics and hospital processes, the use of the Global Location Number grows.
GS1 Healthcare has published a new guide designed to provide implementation assistance for those considering the use of the GS1 Global Location Number in various healthcare settings. This new guide is packed with examples and best practices from use of GLNs from all over the world.
CEN ISO Technical Standard 16791 Health informatics — Requirements for international machine-readable coding of medicinal product package identifiers
The Technical Specification provides guidance about identification and barcoding of packaged medicinal products from the point of manufacture to the point of dispensing.
The purpose of this standard is to link between GS1 and major regulatory initiatives, such as IDMP: Identification of Medicinal Product, and ICSR: Individual Case Safety Report, which are going to be implemented across the world over the next 10 years.. The standard provides guidance to regulatory affairs experts about supply chain processes and needs via use cases designed to support the normative content.
Cooperating standards in healthcare – GS1 standards and other standards cooperating in clinical treatment scenarios
GS1 Healthcare is a neutral and open community bringing together all related healthcare stakeholders to lead the successful development and implementation of global GS1 standards enhancing patient safety, operational and supply chain efficiencies.
We work to help the healthcare sector achieve harmonised implementation of global standards in business and clinical processes enabling interoperability, optimal quality and efficiency of healthcare delivery to benefit patients. To achieve these benefits, GS1 standards can be implemented in an integrated manner with other standards in clinical treatment scenarios. Some examples are shown in this poster.
The perfect hospital: patient journeys and implementing GS1
Hospitals are complex environments delivering specialized medical care to patients.
They are known for the hierarchical and functional complexity of internal stakeholders, and for the combination of processes that support and facilitate clinical care. In a hospital, the GS1 system can greatly support efficiency and change management, leading to increased patient safety and full traceability of pharmaceuticals and medical devices. Following the example of two patient journeys, this poster explains the use of GS1 and some of the stakeholders involved.
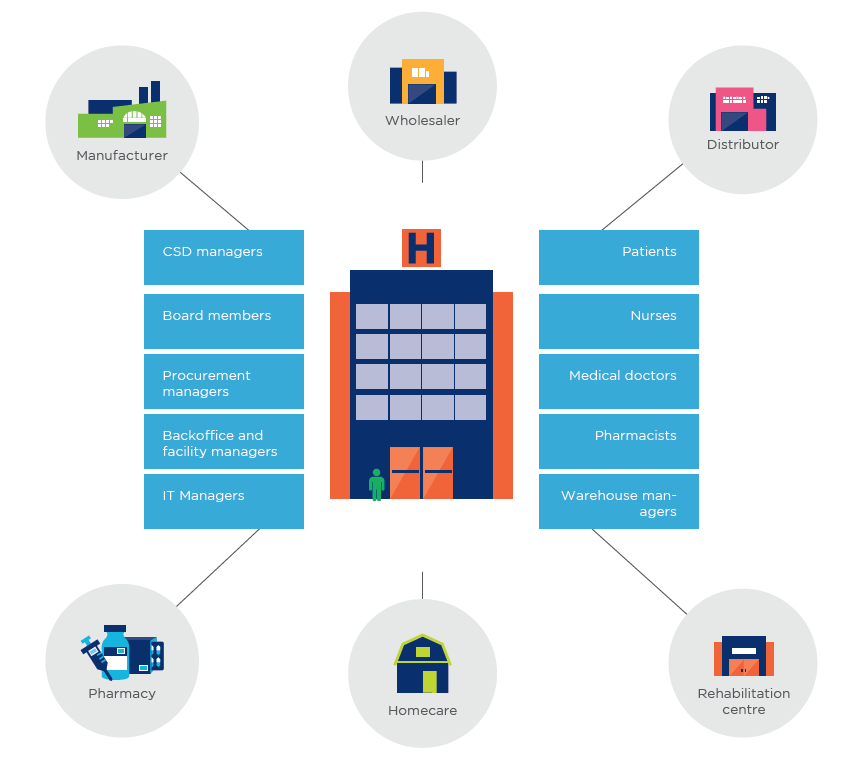
The hospital and its stakeholders
The clinical and care processes within hospitals are supported by several supply chains, logistical, and administrative processes, offering opportunities to start with implementation of GS1.
This poster visualises some of the important internal stakeholders, and is designed to support everyone in engaging with hospitals.